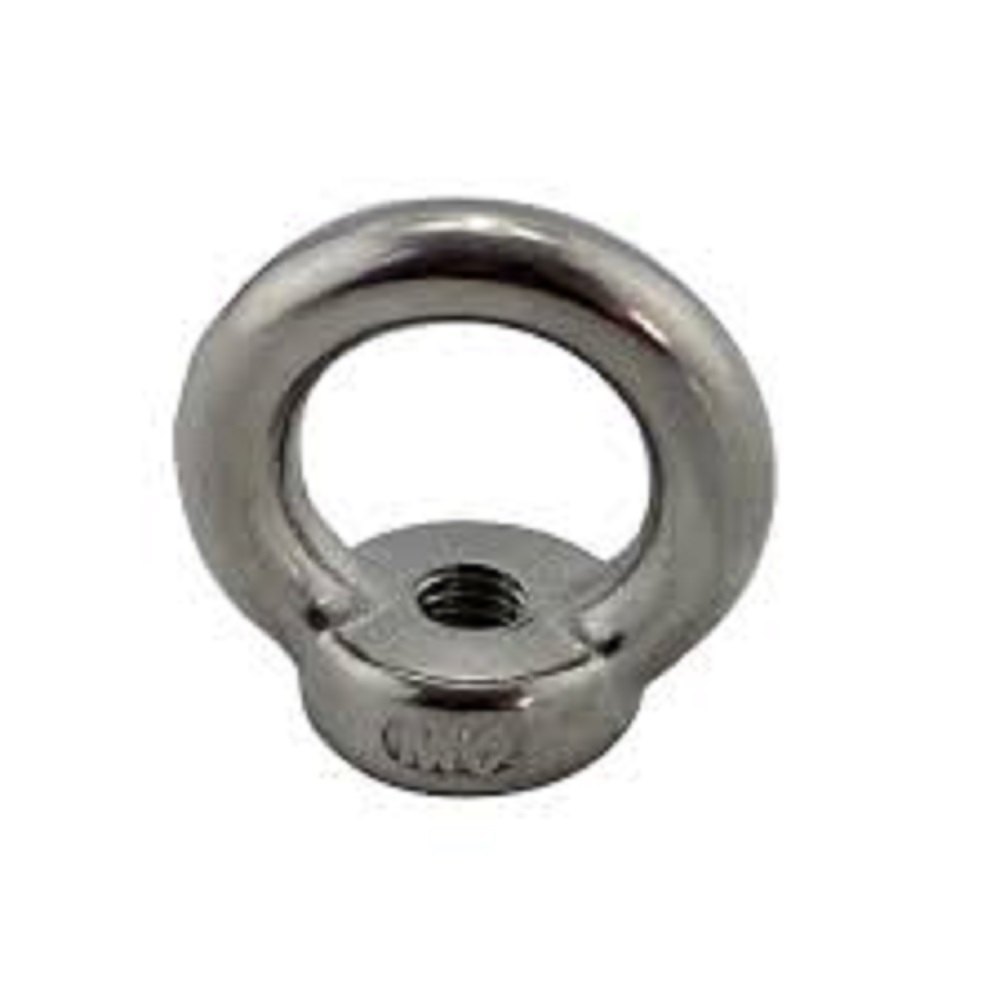
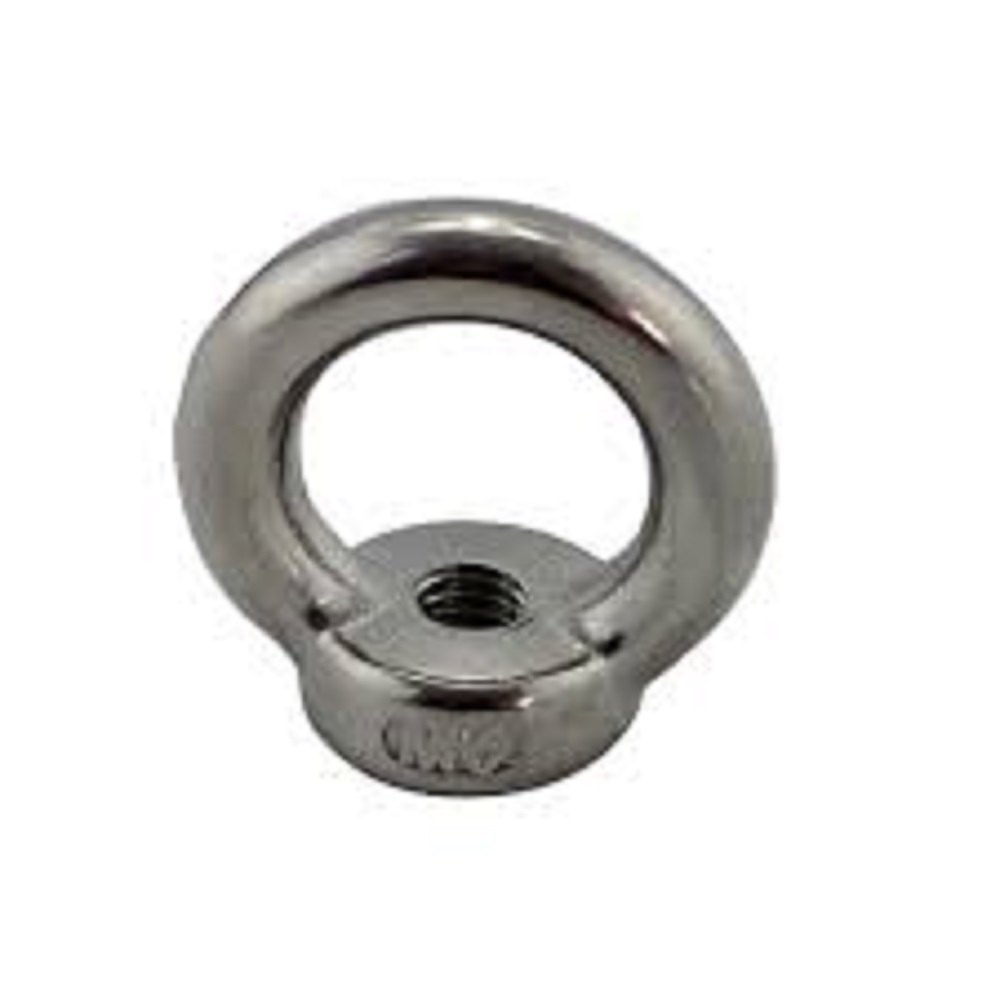
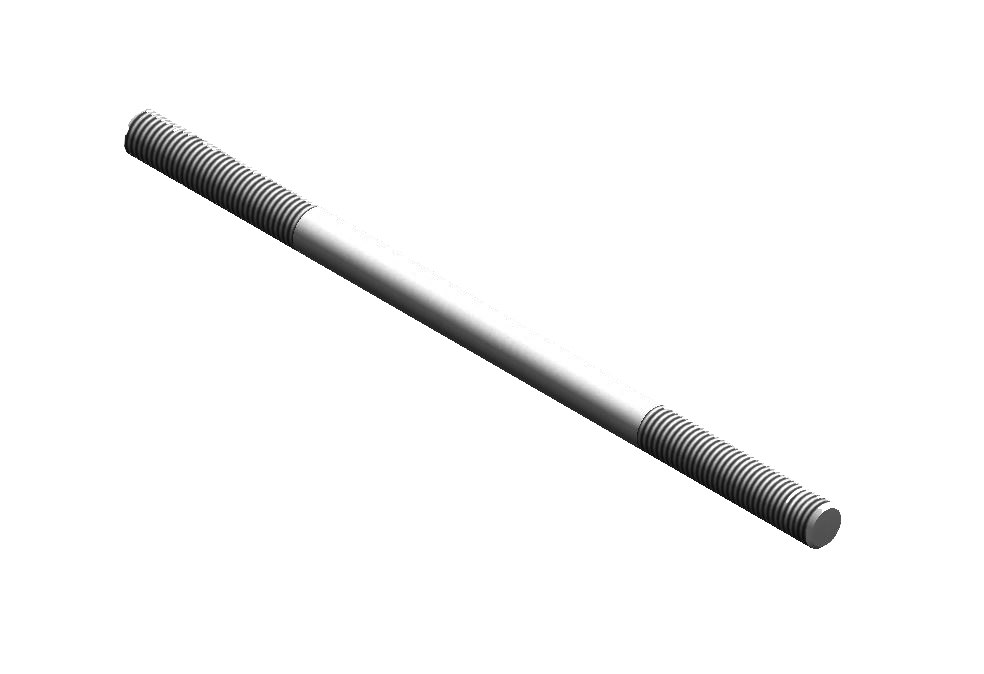
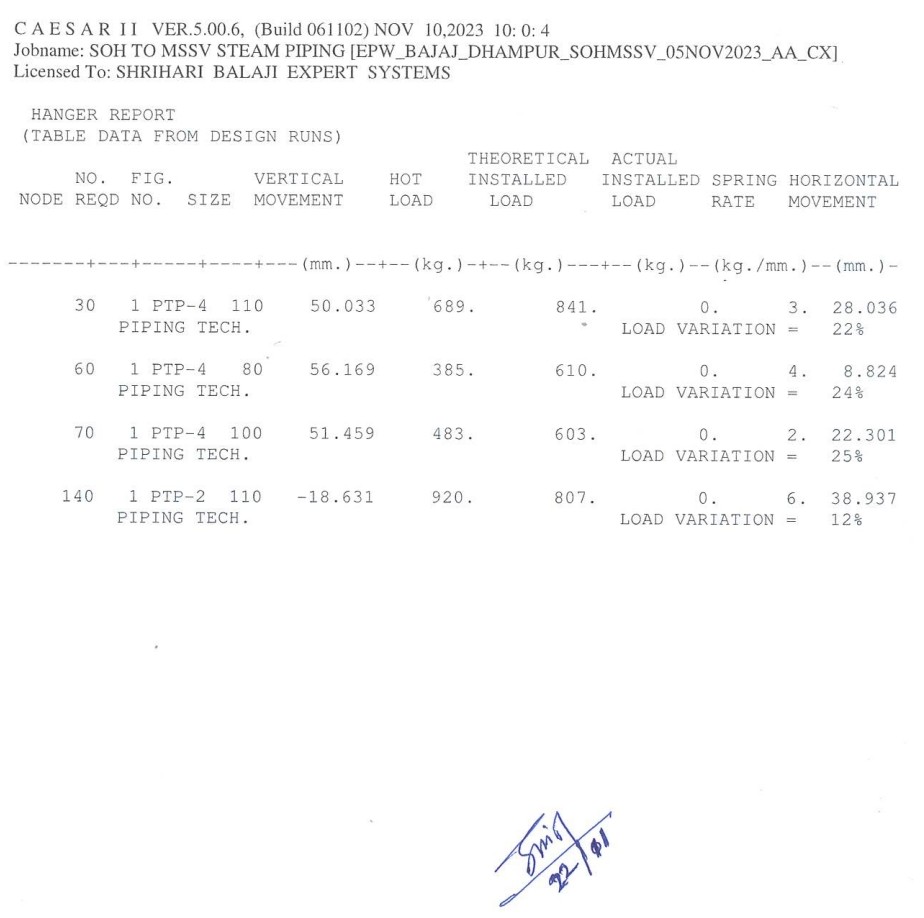
Welded eye nuts are typically made from steel or stainless steel, with 304 or 316 stainless steel being common choices. They are often forged for greater strength, though investment casting is used for some stainless steel eye bolts. The eye nut's internal diameter, overall length, thread length, and bolt diameter are key specifications. Standardized for lifting and rigging applications, they are designed to be used with a nut and washer, and often come with a specified working load limit and safety factor. Key Technical Specifications: Material: Steel (often forged), Stainless Steel (304 or 316). Standard: ISO 3266 (forged eye nuts), EN 1677 (forged lifting components), ASTM F1145 (overhead lifting operations). Dimensions: Internal eye diameter, overall length, thread length, bolt diameter. Working Load Limit (WLL): The maximum load the eye nut can safely support in a straight vertical lift. Safety Factor: A factor of 5 to 1 is typically used for eye bolts. Finishes: Plain, Zinc Plated, Galvanized. Thread: UNC (for some eye bolts). Grade: AISI 410, 12.9 grade eye bolts (for some steel eye bolts). Other Specifications: Dimensions, material requirements, dimensions, and safety factors. Factors Affecting Specifications: Application: Lifting, rigging, etc. Material: Steel vs. Stainless Steel. Load Direction: Axial, angled, etc. Corrosion Resistance: Important for marine and industrial applications. Strength and Durability: Forged steel eye bolts are generally stronger than investment-cast stainless steel eye bolts.